About

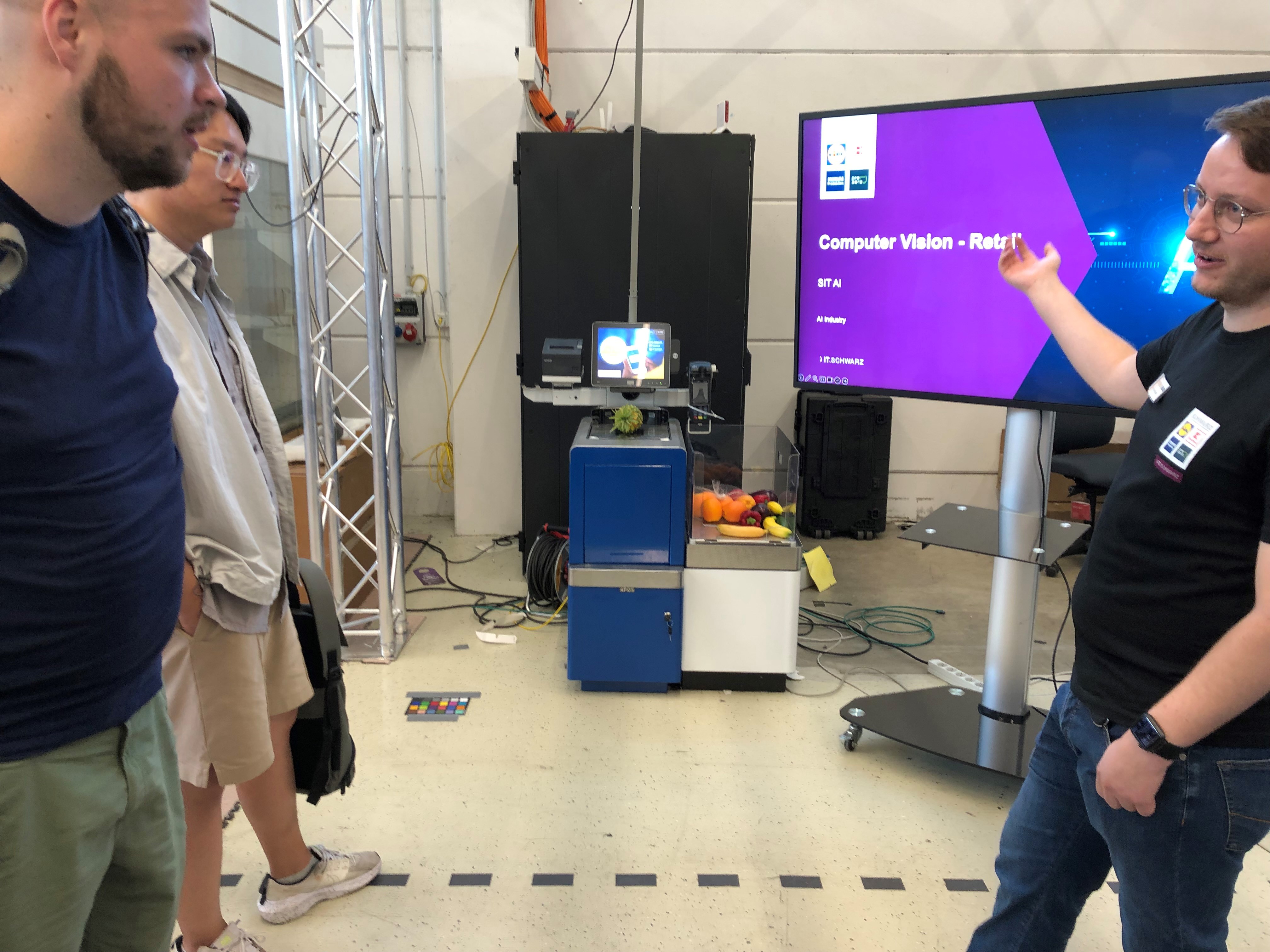
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a key research field in digitalization and holds the potential to drive growth and prosperity in a disruptive way. However, the role of specialized hardware for AI is still underdeveloped: while corporations such as Xilinx, NVIDIA, ARM, and Intel are increasingly integrating AI elements into their platforms, aspects of AI hardware are barely covered in university education. Dedicated AI-capable hardware is particularly relevant in Germany, as—unlike cloud processing—it does not rely on the collection of data in the cloud, which is problematic from a data protection standpoint.
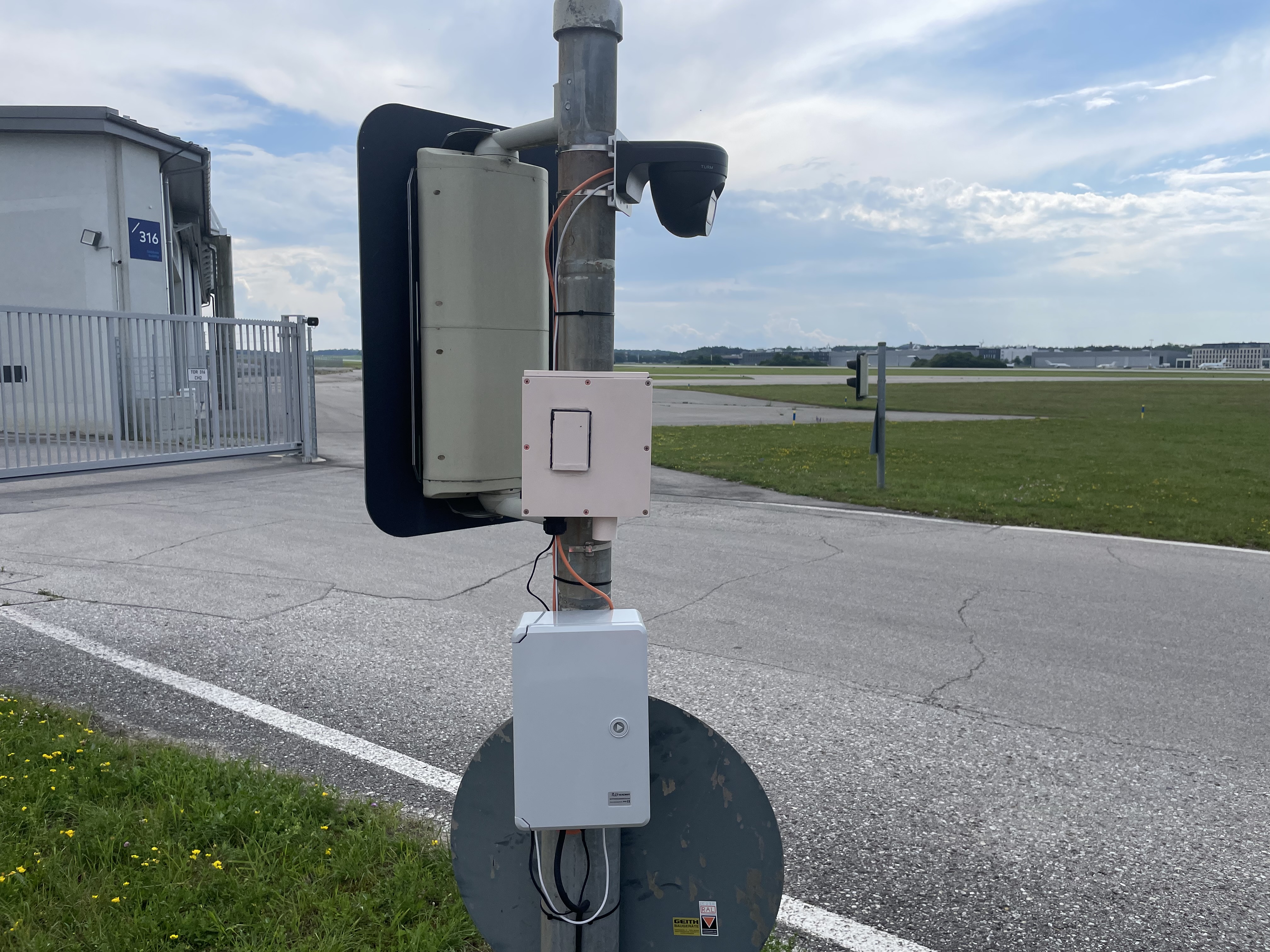
To align our sociopolitical values—such as the right to privacy, informational self-determination, and data federalism—with data-driven innovation (Industry 4.0, 6G, smart cities, autonomous driving, IoT, monitoring via remote sensing and geodata), edge computing is required. In edge computing, the processing of sometimes highly sensitive information takes place where it originates (“network edge”), and only necessary information is transmitted.
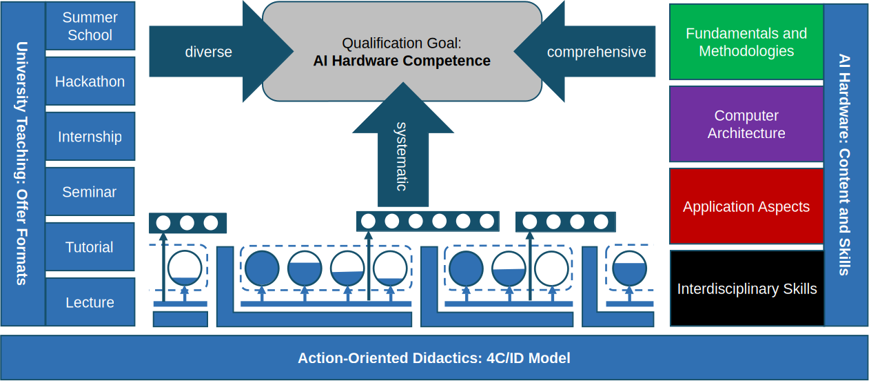
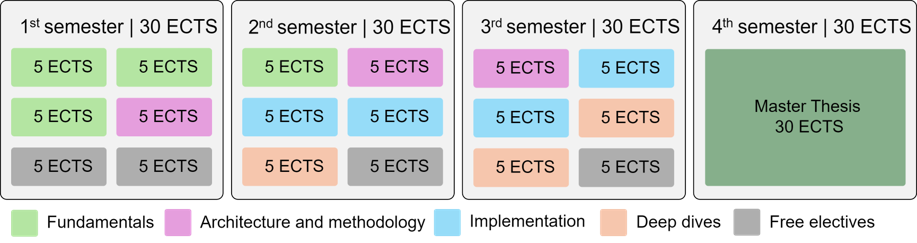
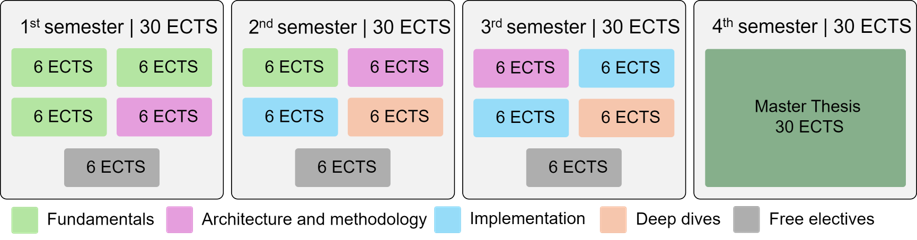
Current university teaching touches only minimally on AI hardware topics due to disciplinary separation. This is where our project aims to make a difference. We seek to address a multidisciplinary target audience (from hardware, AI, and application domains) in an integrative way (through open courses, practice-oriented teaching, and teamwork) and in a realistic context (chip production in Germany, including by students as part of the curriculum). Specifically, we are planning a hybrid, cross-university educational program that combines theoretical foundations, design, and exemplary applications.
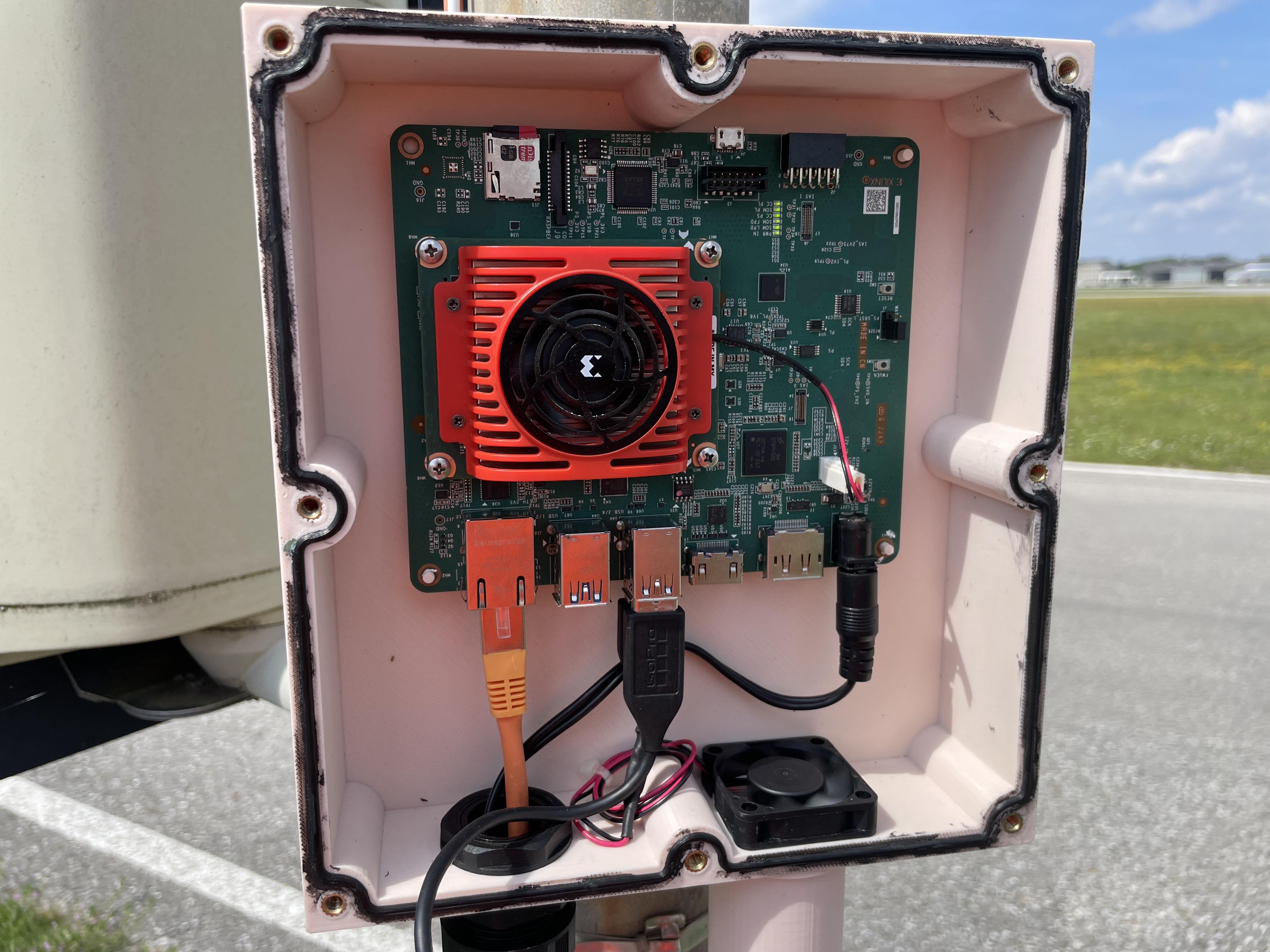
Our consortium, with the affiliated Leibniz Institute IHP in Frankfurt (Oder), offers a unique opportunity in Germany for chip manufacturing, allowing students to practically implement AI hardware during their studies.
Funding: 4 million euros from BMFTR (2021-2025).
Consortium members:
- University of Potsdam:
- Prof. Dr. Benno Stabernack, Institute of Computer Science
- Prof. Dr. Milos Krstic, Institute of Computer Science (overall project lead)
- Prof. Dr. Oliver Korup, Institute of Environmental Science and Geography
- Prof. Dr. Ulrike Lucke, Institute of Computer Science
- Technical University of Munich:
- Prof. Dr. Carsten Trinitis, School of Computation, Information and Technology
- Prof. Dr. Daniel Cremers, School of Computation, Information and Technology
- Prof. Dr. Martin Schulz, School of Computation, Information and Technology
- Prof. Dr. Martin Werner, School of Engineering and Design
Funder